I hear the Autonomous Database upgrade from 19c to 26ai is as easy as a click of a button. Let’s see what is involved and how long it takes.
As part of ongoing platform modernization efforts, upgrading to the latest long-term support release is essential. I initiated the upgrade of my Autonomous AI Database, ABC19CPRD, moving from Oracle Database 19c to 26ai.
Currently, the environment is architected for high availability and disaster recovery across two regions:
Primary Instance: Located in US Midwest (Chicago).

Local Protection: I also maintain a backup-based local peer for an extra layer of redundancy.

Remote Standby: A peer database, ABC19CPRD_IAD, is active in US East (Ashburn) using Autonomous Data Guard.


As you can see, the database is currently 19c, and Oracle shows the “Schedule upgrade to 26ai” option to initiate the upgrade.

One interesting detail in the OCI console is that the upgrade must be orchestrated from the source. If you attempt to schedule the upgrade from the standby instance in Ashburn, OCI reminds you that upgrades can only be scheduled on the Primary database.
Once I navigated back to the Chicago primary, the process was straightforward:
Warning Awareness: OCI provides a clear warning that the database will experience a few minutes of downtime and, importantly, that attached standby databases will be upgraded along with the source.

I chose the “Schedule upgrade to 26ai” option and opted for the “Earliest available schedule” to get started immediately.

Oracle provided the schedule within a few minutes, and it is supposed to start at 11:00 PM UTC. The primary database state transitioned to “Updating”.

The same was visible on the standby side as well.

Looking at the Work Requests, I can see the operation “Update Autonomous AI Database scheduled time for DB upgrade to 26ai” is currently in progress.

The upgrade on the primary instance, ABC19CPRD, was the first to move, starting at 11:00:14 PM UTC. It successfully finished its version transition just four minutes later, at 11:04:03 PM UTC.


The version information in the OCI Portal was updated to show 26ai.

A query of the banner in V$VERSION confirms the new identity: Oracle AI Database 26ai Enterprise Edition Release 23.26.1.1.0.

A few minutes after the primary upgrade, standby still shows 19c. Scheduled 26ai upgrade time is the time I scheduled for the primary upgrade.

After a few minutes, the standby upgrade kicked off.

I am skeptical of the standby upgrade time – it started and finished immediately according to the work request, but the standby had “Updating” status at the top for 4+ minutes.

After about 15 minutes of total elapsed time from start to finish, the environment was fully upgraded to 26ai.

Both the Chicago and Ashburn consoles now proudly display Database Version: 26ai.
Oracle also initiated the automatic backup shortly after the primary upgrade.

This is one issue when people use the version in the database name – now my 26ai database is named 19c! Luckily, Autonomous offers an easy way to change the display name. It only changes the display name; the database name remains the same.


But my autonomous data guard standby instance still has the old display name, and there is no option to change its name.
That’s it. 15 minutes to upgrade the Autonomous AI Database Serverless from 19c to 26ai.
Behind the Scenes: Why the Upgrade Is So Fast
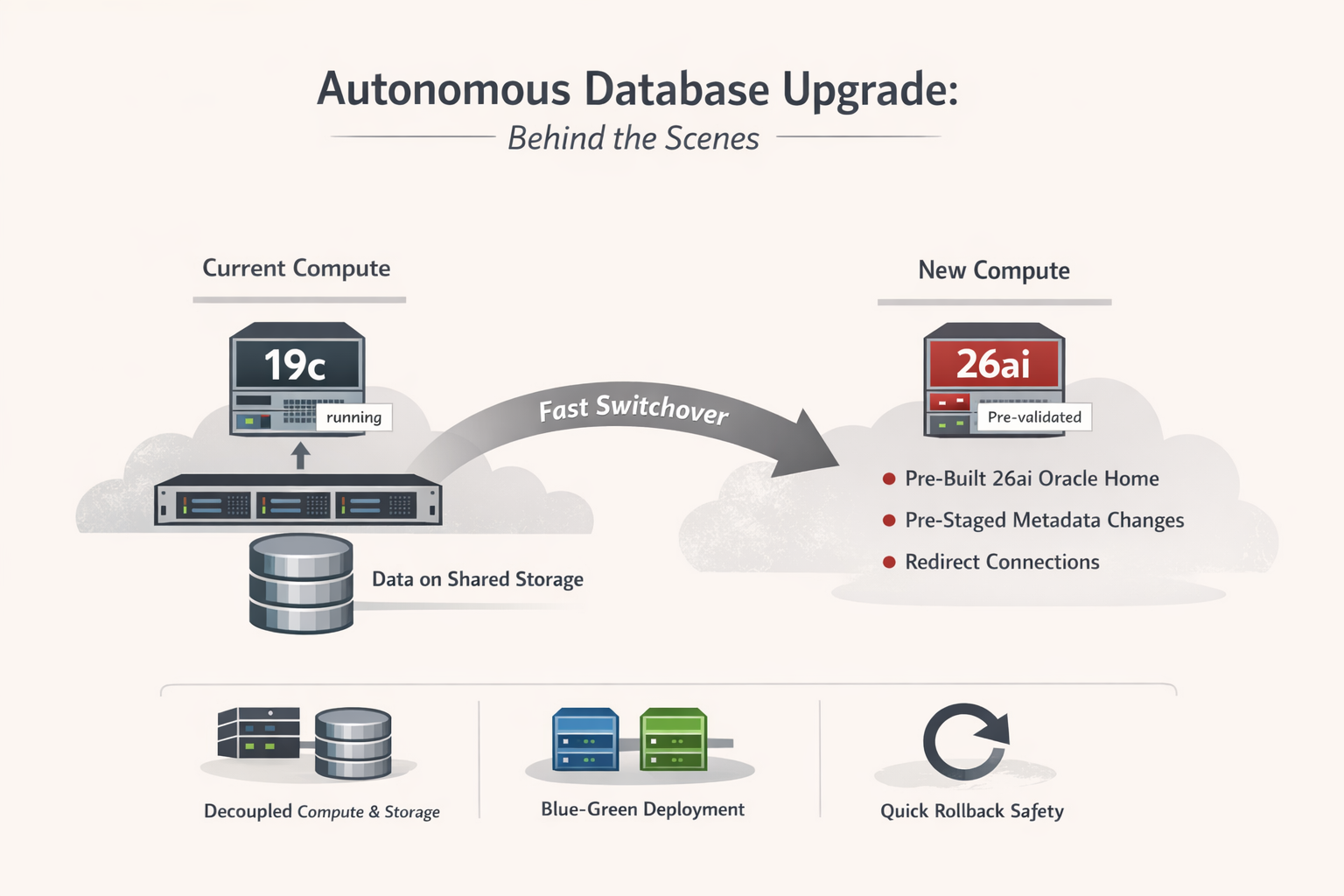
What makes the Autonomous Database upgrade from 19c to 26ai finish in minutes is that it is not a traditional in-place database upgrade.
In Autonomous Database, compute and storage are decoupled. The database files live on Exadata storage, while the database engine runs on disposable compute. During an upgrade, Oracle does not upgrade binaries in a running database. Instead, Oracle switches the database to a new, pre-provisioned compute stack that is already running the 26ai engine.
The 26ai Oracle Homes are built, patched, and validated ahead of time across the Autonomous fleet. By the time the upgrade starts, the target engine is already live and tested. The upgrade window is primarily spent draining connections, switching compute, and running final health checks.
Data dictionary and internal metadata changes are also handled differently. Many transformations are pre-staged or deferred, and several 26ai capabilities are enabled only when first used. This avoids the long-running dictionary upgrade steps that dominate traditional upgrades.
In short, the speed comes from architecture, not faster scripts. Autonomous Database upgrades work because Oracle controls the full stack and treats the database engine as a replaceable component rather than something that must be upgraded in place.
Rollback and Alternate Upgrade Options
Once a scheduled upgrade is initiated in Autonomous Database, it cannot be paused or cancelled, and there is no self-service downgrade option after completion. However, Oracle does provide a limited rollback window (via Oracle Support) if issues are identified shortly after the upgrade, which is possible because the upgrade does not modify data in place. For customers who want to reduce risk further, Oracle also supports full clone and refreshable clone–based upgrades. A refreshable clone allows you to validate application behavior on 26ai while continuously syncing data from the 19c primary, making it ideal for pre-production testing. A full clone, on the other hand, creates a one-time copy that can be upgraded independently and used for functional validation or performance testing before committing to the production upgrade. These options provide a practical safety net when upgrading business-critical workloads.